Observation and Measurement of Foundation Using Digital Microscopes
This section provides an overview of foundation and introduces examples of its observation and measurement using a digital microscope.

- What Is Foundation?
- Foundation Types and Characteristics
- Foundation Roles
- What Is Mineral Foundation?
- Observation and Measurement Examples of Foundation Using a Digital Microscope
What Is Foundation?
Foundation not only makes skin look beautiful by concealing items such as spots and freckles but also protects the skin from ultraviolet rays and other harmful effects. Foundation is generally made from powder (pigments for adding colour), oil, and water, and differences in the oil content make it easier or harder for the makeup to deteriorate.
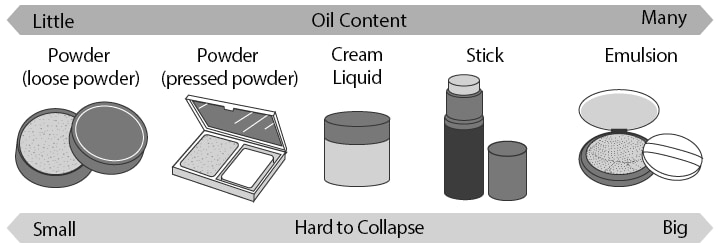
Foundation Types and Characteristics
- Emulsion foundation
- This foundation is a hardened mixture of powder and oil. It is applied to the skin with a sponge or brush, making its intensity easy to adjust and giving it high coverage.
- Stick foundation
- This foundation is a hardened mixture of powder and oil and is provided as a stick. It is applied to the skin directly from the stick, making its intensity easy to adjust and giving it high coverage.
- Cream foundation
- This foundation has more water than emulsion and stick foundations, giving it a high moisturising ability. When applied, this foundation gives long periods of relief from the feeling of dry skin, making it suited to people who suffer from dry skin.
- Liquid foundation
- In the same manner as cream foundation, this foundation can be easily applied to skin whether it is dry or not. Even without a sponge or brush, this foundation can be applied with beautiful results.
- Powder foundation (pressed powder)
- This is a hardened foundation formed by pressing powder. It is suited to people who only want to apply a light amount of foundation, but it is not suited to people who suffer from dry skin.
- Powder foundation (loose powder)
- This foundation is formed from powder that has not been hardened. It is suited to people who only want to apply a light amount of foundation, but it is not suited to people who suffer from dry skin.
Foundation Roles
- Beautification
- Foundation can be used to make the surface of the skin uniform and conceal items such as spots and freckles.
- Moisturising
- The moisturising properties and coverage of foundation make it effective for people who suffer from dry skin.
- Skin protection
- Foundation can protect the skin from ultraviolet rays, dust, pollen, fine particulate matter, and bacteria.
- Anti-ageing
- Because it contains components for beauty treatment, foundation can maintain skin health.
What Is Mineral Foundation?
The main components of mineral foundation are minerals, so it requires no preservatives, leading to a lower load on the skin than general foundations. Not being oil-based, it also has the advantage of not requiring a cleansing agent.
Typical mineral components and characteristics
- Titanium oxide
- This white pigment has the effect of dispersing ultraviolet rays (especially UV-B).
- Zinc oxide
- This white pigment has the effect of dispersing ultraviolet rays (especially UV-A).
- Iron oxide
- This coloured pigment is used to adjust the colour.
- Mica
- Provides glossiness and smoothness.
- Silica
- With excellent absorbency, this component provides a soft texture.
Observation and Measurement Examples of Foundation Using a Digital Microscope
These are the latest examples of observation and measurement of foundation using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K Digital Microscope.
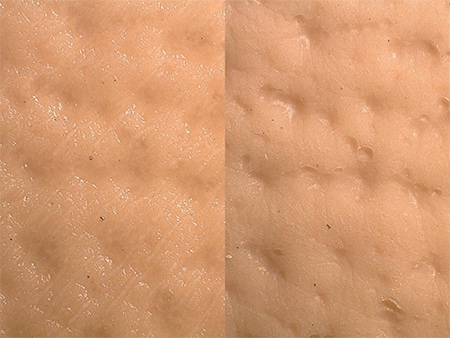
The Multi-lighting function can be used to clearly view the subtle textures of the skin as well as how the foundation has been applied.

The depth composition function can be used to observe the foundation powder.
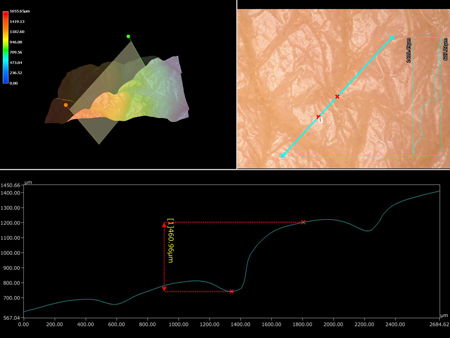
3D profile measurements of skin can be performed with no need to use a replica.
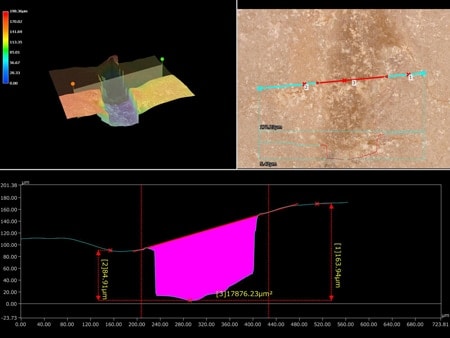
3D profile measurements can be used to quantify pore clogging.